Anúncios
In the rapidly evolving world of healthcare, technology is playing an increasingly crucial role in redefining patient care and medical treatment. This post is poised to delve into the profound impacts of this paradigm shift, exploring the key ways in which technology is revolutionizing healthcare systems and practices across the globe.
From telemedicine to artificial intelligence, innovative technologies are no longer just concepts from a science fiction novel. They are currently being leveraged to improve diagnosis, treatment, and overall patient care. Further on, we will delve into the various ways these technologies are being harnessed to transform healthcare, illuminating the potential they hold for the future.
Anúncios
Additionally, the advent of big data and health informatics has given rise to more personalized and efficient patient care. Through the lens of these advancements, we will examine the unprecedented access to patient information they provide, enabling healthcare professionals to make informed decisions that optimize patient outcomes.
Finally, despite the immense benefits, these technological innovations also present challenges and ethical considerations that cannot be overlooked. In the concluding sections, we will unpack some of these concerns, and the ways in which the healthcare sector is striving to address them. So, buckle up for an insightful exploration into the transformative role of technology in healthcare. 🚀🏥
Anúncios
The Incorporation of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Healthcare
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force across a wide range of industries, and in the realm of healthcare, its impact is proving to be nothing short of revolutionary. By enhancing diagnostic precision, streamlining administrative workflows, optimizing patient care, and facilitating data-driven decision-making, AI is rapidly reshaping the way healthcare services are delivered and experienced. What was once the subject of speculative science fiction is now a tangible reality in hospitals, clinics, and research institutions around the world.

AI systems, particularly those powered by machine learning and deep learning algorithms, have demonstrated an extraordinary ability to analyze vast amounts of data with speed and accuracy far beyond human capability. These capabilities are enabling healthcare professionals to detect diseases earlier, manage treatments more effectively, and ultimately improve patient outcomes across the board.
AI in Medical Diagnosis
One of the most promising and impactful applications of AI in healthcare lies in medical diagnosis. Traditional diagnostic methods, while effective, can be time-consuming, resource-intensive, and prone to human error. AI addresses these limitations by applying sophisticated pattern recognition to large datasets, including medical imaging, electronic health records (EHRs), and genomic data.
For instance, in radiology, AI algorithms trained on thousands of medical images can detect subtle anomalies in X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs with impressive precision. These tools can identify potential signs of diseases such as cancer, pneumonia, or brain hemorrhages, often flagging conditions that might be missed by even the most experienced radiologists. By serving as an intelligent second opinion, AI enhances diagnostic accuracy while also speeding up the process—crucial in time-sensitive scenarios like stroke or trauma care.
Beyond imaging, AI is also being used in pathology to analyze biopsy samples and identify cancerous cells. In dermatology, AI-powered apps can assess skin lesions and suggest whether a mole may require further examination. Furthermore, AI-driven diagnostic platforms are assisting general practitioners in interpreting symptoms and test results to recommend potential diagnoses and next steps, ensuring that care decisions are more informed and consistent.
AI in Predictive Analytics and Risk Stratification
AI doesn’t just diagnose existing conditions—it can also anticipate future health risks. Through predictive analytics, AI models assess a patient’s risk of developing chronic illnesses by analyzing lifestyle data, genetic predispositions, medical history, and even social determinants of health. These insights enable clinicians to implement early interventions and preventive care strategies tailored to the individual, potentially reducing long-term healthcare costs and improving quality of life.
Hospitals and insurers are already leveraging predictive algorithms to identify high-risk patients who are likely to be readmitted within 30 days or experience complications post-surgery. With this information, healthcare teams can proactively adjust treatment plans or provide targeted support to reduce avoidable outcomes.
AI in Patient Monitoring and Care
Another major contribution of AI in healthcare is in continuous patient monitoring and real-time care management. The integration of AI with wearable technologies—such as smartwatches, biosensors, and fitness trackers—has opened new avenues for non-invasive and personalized health monitoring.
These AI-powered devices collect data on a range of health indicators including heart rate, blood glucose levels, oxygen saturation, physical activity, and sleep patterns. Through intelligent algorithms, this data is continuously analyzed to detect abnormal patterns and provide early warnings of potential health issues. For example, a sudden irregularity in heart rhythm detected by a wearable may trigger an alert, prompting immediate medical attention and potentially preventing a life-threatening event.
In chronic disease management, this kind of remote patient monitoring (RPM) has become indispensable. Patients with conditions like diabetes, hypertension, or congestive heart failure benefit from AI systems that monitor their condition in real time and offer personalized feedback or recommendations. These systems can remind patients to take medication, suggest lifestyle adjustments, and notify caregivers or doctors when intervention is needed. This not only enhances patient engagement but also reduces hospital admissions and improves long-term health outcomes.
AI in Clinical Decision Support and Workflow Optimization
Beyond diagnostics and monitoring, AI is enhancing the decision-making process for healthcare providers. Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) integrate AI to assist physicians in selecting appropriate treatments, prescribing medications, and avoiding potential complications or drug interactions. These systems use data from previous patient cases and current clinical guidelines to recommend evidence-based actions, serving as a powerful tool in complex clinical environments.
AI is also streamlining operational workflows within healthcare institutions. From automating administrative tasks such as appointment scheduling and billing, to optimizing staffing and resource allocation, AI is helping healthcare organizations operate more efficiently. Natural language processing (NLP), a branch of AI, is being used to transcribe and interpret doctors’ notes, making medical documentation more accessible and reducing the burden of paperwork.
Ethical Considerations and the Human Touch
While the potential benefits of AI in healthcare are vast, its integration is not without challenges. Concerns around data privacy, algorithmic bias, and transparency must be carefully addressed. AI systems are only as good as the data they are trained on—if that data lacks diversity or contains historical biases, the resulting algorithms may produce inequitable outcomes. Ensuring ethical use of AI involves rigorous validation, continuous monitoring, and transparent reporting of how decisions are made.
Moreover, while AI can augment medical professionals, it should not replace the human element in care. Empathy, intuition, and nuanced judgment remain irreplaceable aspects of medicine. The ideal approach is one of collaboration, where AI serves as a supportive partner, empowering healthcare providers to deliver better, more informed care while preserving the human connection that is central to healing.
Telemedicine: Redefining Patient Consultation
Telemedicine is a pivotal technological advancement revolutionizing healthcare delivery. It enables remote patient consultation, reducing the need for physical visits and making healthcare more accessible.
Virtual Consultations
Virtual consultations, facilitated by video conferencing tools, provide a viable alternative to in-person appointments. They are particularly beneficial for patients in remote areas with limited access to healthcare facilities. Moreover, in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine has proven instrumental in providing uninterrupted healthcare services while minimizing potential virus transmission.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
Telemedicine also enables Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM), a method of collecting health data from a patient in one location and electronically transmitting it to a healthcare provider in a different location. This has proven especially useful for managing chronic illnesses and post-operative care, as it allows for close monitoring of patients’ health without hospitalization.
Blockchain Technology in Healthcare
Blockchain, while often associated with cryptocurrencies, has immense potential in healthcare. It can address several key challenges in the sector, including data security and interoperability.

Secure Data Management
The decentralized nature of blockchain technology ensures secure and tamper-proof storage of health records. Every transaction on a blockchain is encrypted and added to a chain of previous transactions, enhancing data security. This is particularly important in healthcare, where patient confidentiality and data protection are paramount.
Interoperability and Data Sharing
Blockchain facilitates seamless and secure sharing of health records between different healthcare providers. It enhances interoperability, a long-standing challenge in healthcare, thereby enabling comprehensive and coordinated care.
Technology in Surgical Procedures
Technological advancements have dramatically transformed surgical procedures, making them more precise, minimally invasive, and leading to improved patient outcomes.
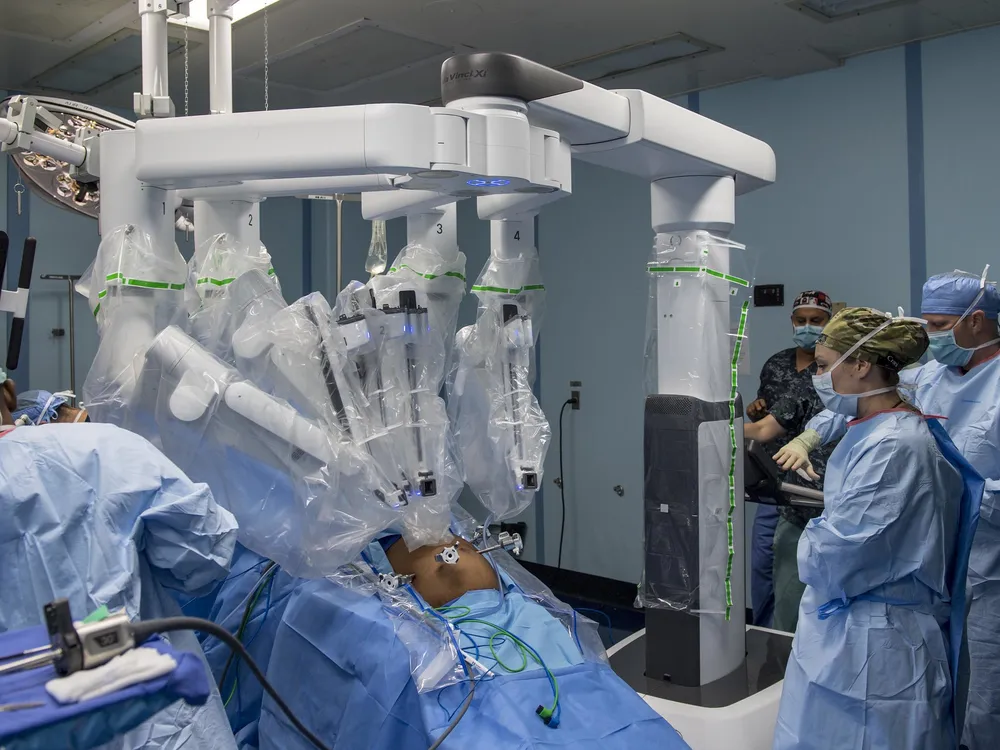
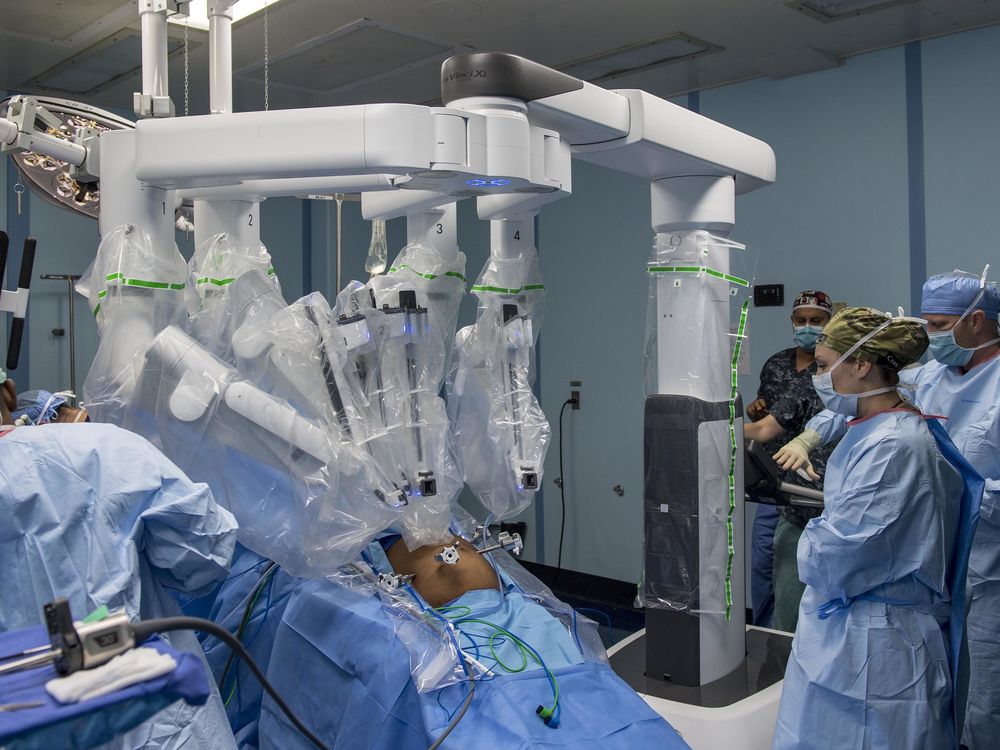
Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery represents a paradigm shift in surgical procedures. It allows for more precision and control, leading to less invasive procedures, minimal scarring, and quicker recovery times. Moreover, robotic surgery can be performed remotely, thus expanding access to specialized surgical procedures.
3D Printing in Surgery
3D printing has a significant role in surgery, particularly in preoperative planning and the creation of personalized prosthetics. Surgeons can use 3D-printed models of the patient’s anatomy to plan and practice surgical procedures, reducing the risk of complications.
These advancements underscore the profound influence of technology on healthcare. From AI-powered diagnostics to telemedicine and blockchain-based health records, technology is revolutionizing medical treatment and patient care, promising a future of healthcare that is more effective, efficient, and accessible.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the role of technology in revolutionizing healthcare is not only pivotal—it is foundational to the future of global health systems. As we’ve explored throughout this discussion, technological innovation has dramatically redefined the way medical treatment and patient care are conceptualized, delivered, and experienced. From the integration of artificial intelligence in diagnostics and patient monitoring, to the widespread adoption of telemedicine and the security offered by blockchain in managing medical records, the healthcare industry is undergoing an unprecedented digital transformation.
This technological evolution has enhanced the efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility of healthcare on multiple levels. It has empowered healthcare professionals with data-driven insights, automated complex processes, and enabled faster and more precise decision-making. Most notably, these advancements have led to a significant improvement in patient outcomes. By harnessing the capabilities of digital health tools and emerging technologies, medical practitioners can now provide more personalized, proactive, and preventive care—fundamentally shifting the focus from treatment to wellness and disease prevention.
One of the most transformative aspects of this shift is the increased accessibility to healthcare services, especially in underserved or remote regions. Telemedicine, virtual consultations, and mobile health platforms have bridged the geographical gap that once limited access to quality care. Patients who previously had to travel long distances or endure months of waiting can now connect with specialists in real time, receive diagnoses, follow-up consultations, and even remote monitoring—all from the comfort of their homes. This level of inclusivity is setting a new standard for global healthcare equity.
Furthermore, the availability of real-time data through wearables and health apps empowers individuals to actively engage in their own health journeys. Patients are no longer passive recipients of care but informed participants, capable of tracking vital signs, medication adherence, physical activity, and more. This democratization of health data encourages greater accountability and healthier lifestyles, contributing to long-term public health benefits.
However, while the benefits of this technological renaissance are vast, it is equally important to confront and address the challenges it presents. Among the most pressing concerns are issues surrounding data privacy and security. The digitization of sensitive health information, although vital for interoperability and convenience, also exposes patients to the risk of data breaches and misuse. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures, implementing strict regulatory frameworks, and maintaining transparency in data usage are crucial steps toward safeguarding patient trust in an increasingly digital healthcare environment.
Another major concern is the digital divide—the gap between those who have access to digital technologies and those who do not. This disparity is particularly evident in low-income or rural communities where internet access, digital literacy, and infrastructure are limited. For technology to truly revolutionize healthcare for all, these inequalities must be addressed through inclusive policies, infrastructure investment, and community education. Without such efforts, technological progress risks exacerbating existing healthcare disparities rather than alleviating them.
Additionally, ethical considerations must remain at the forefront of healthcare innovation. As AI and machine learning systems take on greater roles in clinical decision-making, it is essential to ensure that these systems are transparent, explainable, and free from bias. AI should augment human intelligence—not replace it. Maintaining a human-centered approach ensures that empathy, emotional intelligence, and holistic understanding remain integral to the patient experience. After all, healthcare is not solely a science; it is also a deeply personal and humane practice.
Looking forward, the future of healthcare lies in integration, collaboration, and continuous adaptation. Technologies like precision medicine, augmented reality (AR) in surgical training, genomic analysis, and quantum computing in drug discovery are already beginning to take shape, promising even more groundbreaking changes ahead. But their success will depend on the ability of healthcare systems to evolve—technically, culturally, and ethically. Stakeholders across the spectrum—governments, tech companies, healthcare providers, and patients—must work together to create an ecosystem where innovation thrives and serves the greater good.
To truly harness the potential of these advancements, strategic investment in research and development, interdisciplinary collaboration, and education of healthcare professionals will be critical. As technology evolves, so too must the skillsets and mindsets of those who use it. Training programs that integrate medical knowledge with technological literacy will ensure that practitioners are equipped to use these tools effectively, safely, and compassionately.
Moreover, policy frameworks must be agile enough to accommodate emerging technologies while upholding standards of quality, equity, and ethics. Governments and health institutions must prioritize digital health as a national agenda, encouraging innovation while protecting the rights and well-being of patients.
In essence, the digital revolution in healthcare is not merely about introducing new tools or platforms—it represents a paradigm shift in how we view health itself. It is about empowering individuals, optimizing systems, and building a future where healthcare is not only more advanced but also more humane, equitable, and inclusive.
Embracing this revolution is not an option—it is a necessity. As the world faces increasing healthcare demands due to aging populations, rising chronic diseases, and global health crises, technology offers a lifeline to scalability, sustainability, and resilience. Those who adapt to these changes with foresight and empathy will be at the forefront of shaping the next era in healthcare.
So let us step into this future with open minds and unwavering commitment. The journey toward a smarter, more connected, and more compassionate healthcare system has already begun. And while the road ahead may be complex, the destination—a healthier, more accessible world for all—is well worth the effort.
💡🌐🩺🚀 The digital revolution in healthcare is here. Let’s embrace it—and lead it—with purpose.