Anúncios
Dive into the dynamic world of cloud storage, where accessibility meets seamless data management. As the digital era accelerates, managing and accessing vast amounts of data can seem like an uphill task. However, cloud storage presents a groundbreaking solution, unlocking a plethora of possibilities for businesses and individuals alike. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on how to harness the full potential of cloud storage for enhanced data management and accessibility.
Cloud storage is reshaping the way we store, manage, and access data. With its unrivalled scalability, cost-effectiveness, and easy access from anywhere at any time, cloud storage is redefining data management norms. But how can one leverage this power-packed tool to its fullest? This guide will unpack the intricacies of cloud storage, from understanding its benefits to exploring its potential challenges and the best practices to adopt for effective data management.
Anúncios
So, whether you’re a business owner looking to transition to cloud storage, an IT professional aiming to stay abreast of the latest advancements, or a tech enthusiast curious about cloud storage, this guide will serve as a valuable resource. Get ready to unlock the power of cloud storage and embark on a journey towards seamless data management and accessibility. 🌐💾🔓
The Foundation of Cloud Storage
Understanding the fundamental elements of cloud storage is paramount in unlocking its potential. At its core, cloud storage is a model of data storage where the digital data is stored in logical pools. The physical storage typically spans multiple servers (and in some cases locations), with the physical environment being owned and managed by a hosting company.
Anúncios
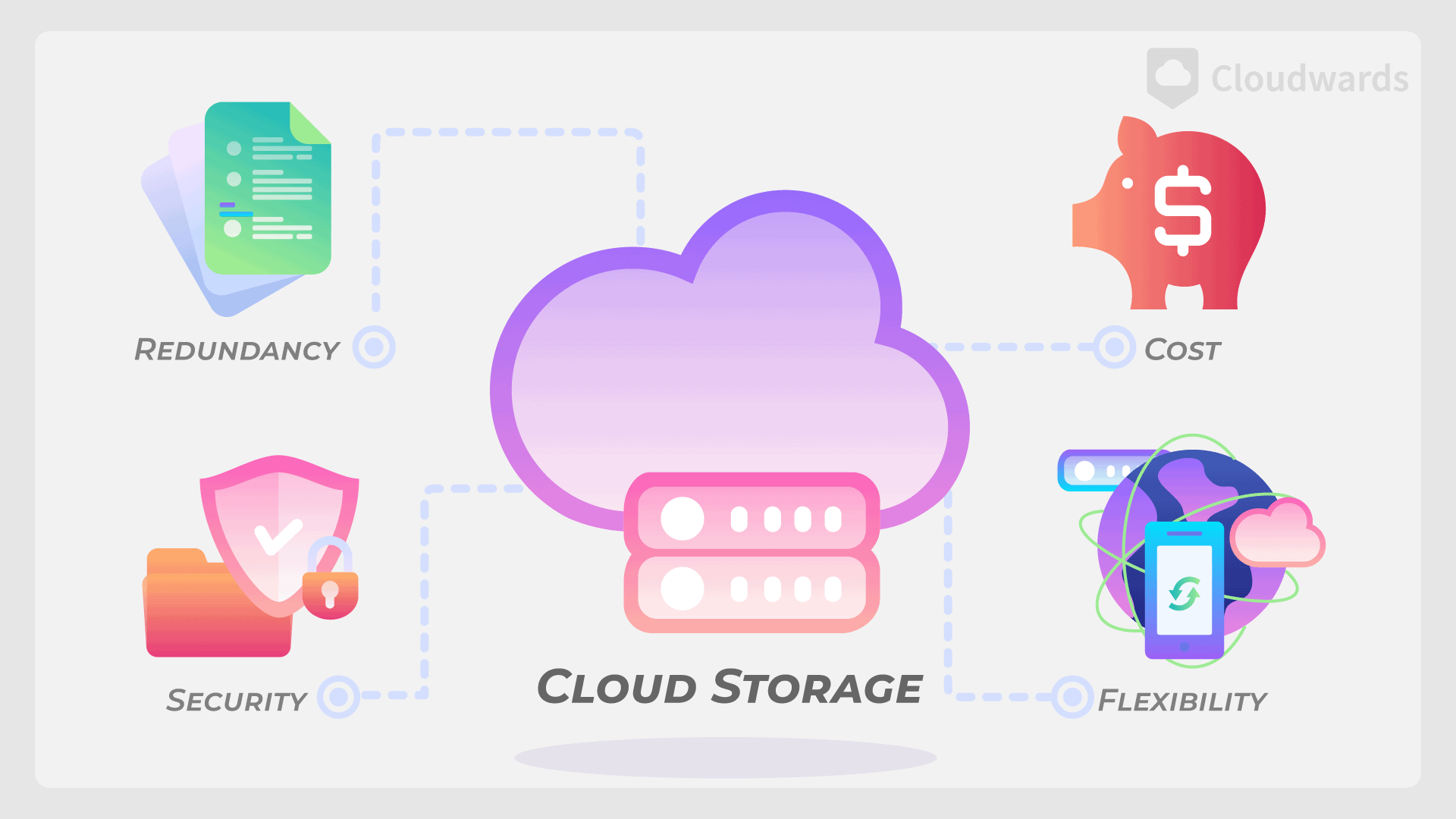
- Public Cloud Storage: This refers to the cloud storage services provided over a network for public use.
- Private Cloud Storage: This form of storage is designed for use within a specific organization, allowing for centralized data storage accessible by various systems and users.
- Hybrid Cloud Storage: This is a combination of public and private cloud storage where some of the data is stored in the in-house infrastructure while the rest is stored in the public cloud.
These different types of cloud storage provide various options for businesses depending on their specific needs, data sensitivity and budgetary considerations.
Essential Components of Cloud Storage
Cloud storage is composed of several essential components that work together to provide seamless data management and accessibility.
Data Security
A crucial aspect of cloud storage is data security. Providers employ a variety of security measures such as encryption, access controls, and secure transmission protocols to ensure that data remains safe from unauthorized access. This is particularly important as data is typically stored across multiple servers, increasing the potential points of vulnerability.
Data Redundancy and Backup
Another essential component of cloud storage is data redundancy and backup. This ensures that your data is not lost in case of any hardware failure, natural disaster, or human error. Most cloud storage providers use techniques like replication and erasure coding to make multiple copies of data and store them on different servers.
Benefits of Cloud Storage
The advantages of cloud storage go beyond simple storage and backup. Some of the benefits include:
Accessibility
With cloud storage, data can be accessed from anywhere, at any time, on any device with internet connectivity. This enhances collaboration and flexibility, particularly for businesses with remote workers.
Cost Efficiency
Cloud storage eliminates the need for businesses to invest in and maintain physical storage infrastructure. You only pay for the storage you use, making it a cost-effective solution.
Scalability
One of the significant advantages of cloud storage is the ability to scale up or down based on the business needs. This level of flexibility is not possible with traditional storage solutions.
Understanding Cloud Storage Pricing
As businesses and individuals increasingly migrate their data to the cloud, understanding the intricacies of cloud storage pricing becomes essential. Pricing is not a one-size-fits-all scenario; it is multifaceted and can vary widely depending on the provider, the type of storage, and the specific services utilized. A well-informed approach to cloud storage pricing ensures that you can optimize your costs while still maintaining the performance, security, and accessibility your operations require.
Tiered Pricing Models
Most cloud storage providers use a tiered pricing structure, where users pay based on the volume of storage consumed. These tiers are typically divided into different levels that reflect storage capacity and features, such as basic storage, infrequent access, and archival solutions.
For example, services like Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, and Microsoft Azure offer tiers such as:
-
Standard Storage: Designed for frequently accessed data and offering high availability.
-
Infrequent Access (IA): Suitable for data that is not accessed often but still needs to be readily available when needed.
-
Archive Storage: Meant for long-term storage of data that is rarely accessed, often at a significantly reduced price point.
Choosing the right tier can dramatically affect your overall expenses. Organizations should regularly analyze usage patterns and move data between tiers accordingly to maximize cost-efficiency.
Per-GB Storage Pricing
At its core, one of the most transparent pricing methods is the per-gigabyte (per-GB) pricing model. In this model, users pay a fixed rate for every gigabyte of data stored, typically calculated monthly. This structure is simple and predictable, making budgeting straightforward.
However, costs can accumulate quickly when storing large volumes of data or if your storage includes numerous backups and versions. In such cases, using data lifecycle policies—automated rules that move older data to cheaper storage tiers—can help reduce costs.
Data Transfer and Bandwidth Costs
An often-overlooked aspect of cloud storage pricing is data transfer, also referred to as egress costs. While many cloud providers allow free or minimal-cost data uploads (ingress), they frequently charge for data downloaded from the cloud to your local environment or shared across regions.
Key considerations include:
-
Outbound data transfer: Data leaving the cloud, such as downloads or data syncing with other servers, may incur fees.
-
Inter-region data transfer: Moving data between regions (for example, from a US server to a European one) can lead to additional charges.
-
API requests: Some providers charge based on the number of operations or requests made to retrieve or manage data.
Understanding how your organization moves data—internally, externally, and across borders—is crucial in avoiding surprise costs. It’s important to assess how frequently data is accessed, and from where, to select the most appropriate pricing plan.
Storage Type and Redundancy
Cloud storage pricing also varies depending on data redundancy and availability requirements. Redundancy refers to the duplication of data across multiple locations or disks to prevent data loss in the event of hardware failure or disaster.
Cloud providers typically offer different levels of redundancy, such as:
-
Single-Region Storage: Keeps data in one geographic region. It’s more affordable but poses a higher risk in case of regional outages.
-
Multi-Region Storage: Stores multiple copies across various regions, ensuring higher availability and disaster resilience, but at a higher cost.
-
Cold Storage: Ideal for archiving, with lower prices and higher latency for retrieval.
Organizations should evaluate their Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) to select the appropriate redundancy model that aligns with both their performance needs and budget.
Hidden Fees and Additional Considerations
In addition to storage and transfer fees, some cloud providers may impose hidden charges that can catch users off guard:
-
Early deletion fees for data stored in cold or archive tiers for less than the minimum required time (e.g., 30 or 90 days).
-
Versioning costs if multiple copies of the same file are stored to enable rollback.
-
Encryption services, although often included, may incur extra charges depending on the provider and encryption level used.
Thoroughly reviewing service agreements and cost calculators provided by cloud vendors can help uncover these potential extra costs.
Optimizing Costs Through Automation and Monitoring
To manage cloud storage costs effectively, organizations can adopt the following best practices:
-
Use cost monitoring tools: Cloud providers often offer dashboards that help you track and analyze usage. Examples include AWS Cost Explorer, Google Cloud Billing Reports, and Azure Cost Management.
-
Implement automation: Automatically moving older data to cheaper storage tiers or deleting unused data through retention policies can reduce storage waste.
-
Leverage reserved capacity: Some providers offer discounts for committing to long-term storage needs, which can be ideal for predictable workloads.
Implementing Data Governance
As organizations increasingly adopt cloud storage solutions, the implementation of strong data governance, efficient migration strategies, and seamless data integration becomes not just beneficial—but essential—for ensuring security, compliance, and productivity.
Implementing Data Governance
Data governance forms the foundation of any successful cloud strategy. It involves a structured approach to managing data assets through clearly defined policies, responsibilities, and procedures. A robust data governance framework ensures that data remains accurate, secure, and compliant with regulatory requirements.
Key elements of effective data governance include:
-
Access Control: Clearly define who can access what data and under which circumstances. Implement role-based access controls (RBAC) to ensure that employees only access data necessary for their responsibilities.
-
Data Classification: Categorize data based on sensitivity and importance. For instance, financial records or personal identifiable information (PII) should be classified as high-priority, requiring stricter controls and encryption.
-
Breach Response Protocols: Establish response procedures in case of data leaks or security breaches. This includes notifying affected parties, conducting a root cause analysis, and revising protocols to prevent recurrence.
With data governance in place, organizations can confidently move forward with cloud adoption while maintaining regulatory compliance and reducing operational risk.
Data Migration
Migrating data to the cloud is a pivotal phase that must be approached with precision and foresight. It involves transferring vast volumes of information from legacy, on-premises systems to cloud environments.
To ensure a successful migration:
-
Develop a detailed migration roadmap outlining timelines, workloads, stakeholders, and risk mitigation plans.
-
Use migration tools offered by cloud providers (like AWS Migration Hub or Azure Migrate) to automate and monitor the process.
-
Test before full migration: Conduct trial runs to identify issues, measure performance, and validate integrity before scaling up.
A poorly executed migration can result in data loss, extended downtime, and disrupted business operations, so careful planning and execution are non-negotiable.
Data Integration
Once data is successfully migrated to the cloud, it must be effectively integrated across systems and platforms to provide value. Data integration ensures that information flows seamlessly between applications, enabling unified access and more efficient workflows.
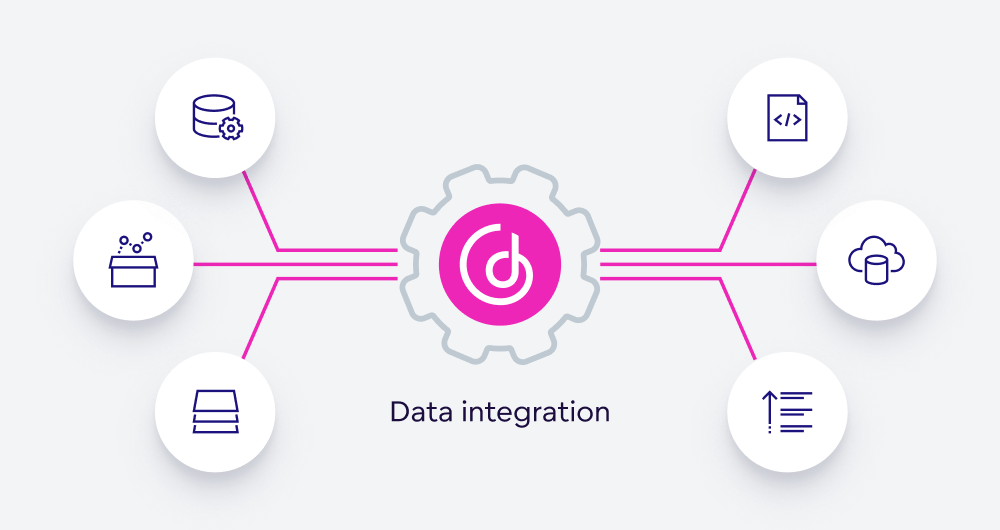
Best practices include:
-
Adopting integration platforms (like MuleSoft, Zapier, or AWS Glue) to synchronize data from multiple sources in real time.
-
Implementing APIs to enable different systems to communicate and share data automatically.
-
Ensuring data consistency by maintaining standardized formats and regular validation routines.
Well-integrated data environments promote collaboration, improve reporting accuracy, and enhance decision-making by giving stakeholders a complete and coherent view of organizational information.
Choosing a Cloud Storage Provider
Choosing the right cloud storage provider is a crucial decision that can have a significant impact on your business. Some factors to consider include the provider’s reputation, security measures, pricing structure, and customer service.
Reputation
Check reviews and testimonials from other clients to get a sense of the provider’s reliability and performance.
Security Measures
Look for a provider that offers robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and secure data transmission.
Customer Service
Choose a provider that offers reliable customer service to handle any issues that may arise.
By understanding the foundation, components, benefits, pricing, and data management of cloud storage, you can unlock its full potential for your business. The right cloud storage solution can lead to enhanced accessibility, cost savings, and effective data management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, leveraging the power of cloud storage offers a multitude of benefits for seamless data management and accessibility. This transformative technology not only provides an efficient and secure way to store data, but also paves the way for enhanced collaboration, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Moreover, with the dynamic nature of cloud storage, users have the liberty to access their data from anywhere, at any time. However, it’s crucial to choose the right cloud storage provider that aligns with your specific needs. Factors such as data security, uptime, customer support, and pricing plans should be diligently considered. While data migration to the cloud may seem daunting, the long-term benefits it reaps makes the journey worthwhile. As technology advances, the power of cloud storage continues to unlock new horizons in data management and accessibility. Harnessing its potential is no longer an option, but a necessity in today’s digital age. Ultimately, embracing cloud storage is embracing a future where data is accessible, manageable, and secure.

